In the world of competitive sports, where every marginal gain counts, athletes have long sought the perfect diet to fuel their bodies and minds. Today, with the rise of plant-based and vegan diets, the question of what constitutes optimal nutrition is more prominent than ever. While many athletes thrive on various dietary regimens, growing evidence shows that animal-based nutrition offers undeniable advantages, particularly for those seeking peak performance.
This is not to dismiss the success of plant-based athletes—many of whom have managed to excel through proper supplementation and careful planning—but rather to explore why a diet rich in animal proteins and fats aligns most closely with the biological needs of athletes and the general population alike. Let’s examine why animal-based nutrition is so vital, the role supplementation plays in plant-based diets, and how the 2024 Olympics became a cautionary tale for those neglecting the nutritional needs of athletes.
The Biological Imperative of Animal-Based Nutrition
The human body has evolved over millennia, and animal-based nutrition has been central to our survival. From hunter-gatherer societies that thrived on the nutrient-dense meats of wild game to modern athletes pushing their physical limits, animal proteins, and fats have consistently provided the essential nutrients humans need to build muscle, recover quickly, and sustain energy.
Complete Proteins for Muscle Growth and Recovery
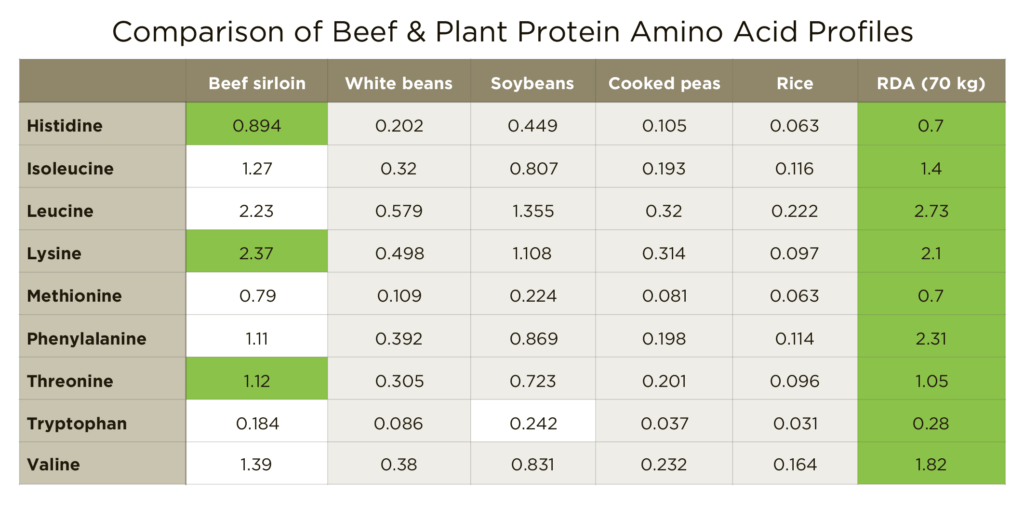
One of the most significant advantages of animal-based foods is their complete protein profile. Animal proteins contain all nine essential amino acids in the exact ratios that the human body needs. These amino acids are the building blocks of muscle tissue and play a critical role in muscle repair, immune function, and energy metabolism—all essential for athletes.
When athletes push their muscles to the limit, whether through intense weight training, endurance sports, or explosive exercises, they rely on protein to rebuild and grow stronger. Research shows that leucine, an amino acid found in animal proteins, plays a vital role in triggering muscle protein synthesis—the process by which the body repairs and grows muscle fibers. Athletes consuming animal-based foods like beef, eggs, and fish can access this amino acid in abundance, allowing for rapid recovery and muscle development.
In contrast, many plant-based proteins lack one or more of these essential amino acids, requiring plant-based athletes to combine different food sources to achieve the same effect. While it’s possible to get all essential amino acids on a plant-based diet, the process is more complex and requires careful planning to avoid deficiencies. Athletes who consume animal proteins, on the other hand, have a more straightforward path to optimizing their recovery and performance.
The Power of Animal Fats for Endurance and Energy
In addition to protein, animal fats play a crucial role in athletic performance. Contrary to the outdated belief that fat is detrimental, recent studies have shown that healthy fats, particularly from animal sources, are essential for long-term energy, hormone production, and brain function. For athletes, consuming sufficient fats ensures they have a steady source of fuel during extended periods of physical exertion.
Animal fats provide a concentrated source of energy that lasts longer than carbohydrates. Fats are metabolized more slowly, providing endurance athletes with sustained energy without the spikes and crashes associated with high-carbohydrate diets. For those competing in marathons, triathlons, or ultra-endurance events, animal fats can be a game-changer, helping to maintain consistent energy levels over hours of exertion.
Beyond energy, animal fats are also vital for hormone production, particularly testosterone and other anabolic hormones that regulate muscle growth and repair. Cholesterol, a precursor to many hormones, is abundant in animal products like eggs and beef. Studies suggest that a diet rich in animal fats supports higher testosterone levels, which are critical for athletes looking to maximize strength and recovery.
Plant-Based Athletes: Supplementation and Success
It’s important to acknowledge that many athletes have achieved remarkable success on plant-based diets. Strongmen, UFC fighters like Nate Diaz, and countless others will often supplement their diets with vitamins, minerals, and proteins to make up for the nutrients lacking in plant foods. Vegan athletes may use protein powders, vitamin B12 supplements, and omega-3 supplements derived from algae to cover gaps that are naturally filled by animal-based nutrition.
Success Through Supplementation
Many plant-based athletes are exceptional not just because of their diet but because they are exceptional athletes who have honed their skills through years of training, discipline, and focus. Their success on a plant-based diet often stems from meticulous planning and using various supplements to avoid nutrient deficiencies.
For example, one of the key challenges plant-based athletes face is the lack of vitamin B12, which is found only in animal products. B12 is critical for energy production, neurological function, and red blood cell formation. Plant-based athletes typically need to supplement this essential vitamin to maintain optimal performance.
Similarly, creatine, a compound found naturally in animal-based foods like red meat, supports explosive power, strength, and recovery. While many plant-based athletes supplement with synthetic creatine, those on animal-based diets naturally consume this compound, further supporting their performance without the need for artificial intervention.
Evidence Supporting Animal-Based Nutrition for Optimal Performance
Though plant-based diets have their place, particularly when supplemented properly, a wealth of evidence supports the idea that animal-based nutrition is optimal for athletic performance. Human beings, by design, are omnivores who have evolved to thrive on a diet that includes animal products. Modern science continues to reveal the profound advantages of consuming nutrient-dense, animal-based foods.
Protein Quality and Muscle Growth
Numerous studies have demonstrated that animal proteins are superior for muscle growth and recovery. A study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition showed that animal-based proteins, particularly from red meat and eggs, were more effective at stimulating muscle protein synthesis compared to plant-based proteins like soy or wheat gluten.
This is particularly important for athletes focused on strength and hypertrophy, as building and maintaining muscle mass requires the most efficient and effective protein sources. Animal proteins provide a complete amino acid profile in an easily digestible form, making them ideal for supporting athletic goals.
The Role of Animal Fats in Cognitive and Physical Performance
Animal fats, particularly those rich in omega-3 fatty acids, are crucial for brain health and cognitive performance. Athletes often overlook the importance of mental sharpness during competition, but cognitive function plays a significant role in athletic success. Omega-3s, found in fatty fish like salmon, support brain function, reduce inflammation, and improve recovery times after intense exercise.
Moreover, animal fats are key to balancing inflammation in the body. While training induces a certain amount of inflammation necessary for adaptation, chronic inflammation can lead to injuries and hinder recovery. Omega-3 fatty acids help to modulate inflammation, ensuring that athletes can recover more effectively between sessions and reduce the risk of overuse injuries.
Raw Milk: A Prime Example of Nutritional Integrity
In my article, “Raw Milk’s Comeback: History, Health, and How to Find It,” I discussed the resurgence of interest in raw milk, a natural, nutrient-dense product that has been unfairly demonized in modern times. Raw milk provides a perfect analogy for how whole, unprocessed animal products support optimal health.
Raw milk is rich in enzymes, vitamins, and probiotics that aid digestion and strengthen the immune system. These beneficial elements are destroyed during pasteurization, leaving consumers with a nutritionally inferior product. The same holds true for the comparison between whole animal-based foods and heavily processed plant-based alternatives.
Just as raw milk retains its full nutritional integrity, so too do grass-fed beef, wild-caught fish, and pasture-raised eggs. These foods provide athletes with all the nutrients they need without the downsides of processing, additives, or artificial supplements. The more we return to whole, unprocessed animal products, the more we align with nature’s intended form of nutrition.
Plant-Based Meat and the Rise of Processed Foods: A Comparison
In “Dark Side of the Plant-Based and 3D-Printed Fake Meat Industry”, I discussed the rise of plant-based and fake meat alternatives. These products, often marketed as healthy and sustainable, are little more than heavily processed foods filled with chemical additives, preservatives, and synthetic nutrients. We explored how the fake meat industry preys on the craving for real meat by offering highly processed substitutes that fail to provide the complete nutrition found in whole animal foods.
Many fake meats, such as those made with soy protein isolate or pea protein, undergo extensive processing that strips away much of their nutritional value. While these products mimic the taste and texture of meat, they cannot replicate the bioavailability of nutrients found in real animal products. Soy protein isolate, for example, is often stripped of its natural nutrients and filled with additives to create a meat-like texture.
The Environmental Myth: Sustainability and Animal-Based Foods
Both of your articles emphasize that while sustainability is a valid concern, real, unprocessed animal-based foods—especially when produced through regenerative farming—are more environmentally friendly and nutrient-dense than highly processed alternatives. As you explored in “Dark Side of the Plant-Based and 3D-Printed Fake Meat Industry”, the idea that plant-based and fake meats are the answer to environmental concerns is flawed. Monoculture farming, necessary for large-scale production of plant-based foods, depletes the soil and relies on chemical fertilizers and pesticides that harm the environment.
Conversely, regenerative farming practices that prioritize grass-fed livestock can actually improve soil health, sequester carbon, and support biodiversity. This creates a sustainable food system where both the environment and the consumer benefit. Athletes who consume products from regenerative farms are getting superior nutrition and contributing to a more sustainable food chain—a balance that fake meat and highly processed plant-based foods cannot achieve.
The 2024 Olympics: When the Plant-Based Push Failed Athletes
The 2024 Paris Olympics serve as a real-world example of what happens when athletes are deprived of high-quality animal-based nutrition. In an effort to promote sustainability, the Olympic Village prioritized plant-based foods, drastically reducing the availability of animal products. Athletes, already dealing with subpar living conditions, were left with insufficient protein and caloric options to fuel their performances.
According to a report by The Hill, many athletes complained about the lack of adequate nutrition, particularly regarding the high-protein, high-calorie meals they required. Some teams had to fly in their own chefs and food supplies to ensure their athletes had access to nutrient-dense meals, emphasizing the limitations of a plant-based approach in the context of elite sports.
While the intent behind the plant-based push was to reduce the games’ carbon footprint, the result was a nutritional disaster for many athletes. The lack of animal-based nutrition left athletes scavenging for meat, and the performance impact was noticeable.
Striking a Balance: Why Animal-Based Diets Are Still Essential
While plant-based diets can work for some athletes, particularly with careful supplementation, the evidence overwhelmingly supports the idea that animal-based diets provide the most complete and bioavailable nutrition for optimal performance. For athletes looking to push their limits, recover quickly, and maintain long-term health, the nutrient density and biological compatibility of animal products simply cannot be replaced.
Animal-based nutrition aligns with the evolutionary design of human physiology, providing essential amino acids, fats, vitamins, and minerals in their most efficient form. While plant-based diets require supplementation and careful food combinations to cover nutritional gaps, animal-based diets offer a straightforward, natural approach to meeting the complex needs of athletes.
Conclusion: The Case for Animal-Based Nutrition in Athletics
As the world of sports continues to explore various dietary trends, it’s becoming increasingly clear that animal-based nutrition remains the gold standard for athletic performance. While many athletes have found success on plant-based diets through meticulous planning and supplementation, the human body is naturally wired to thrive on a diet rich in animal products.
From complete proteins and bioavailable nutrients to essential fats that support brain function and hormonal health, animal-based foods offer the most comprehensive nutrition for athletes aiming to perform at their peak. Whether for strength, endurance, or recovery, animal proteins and fats provide the building blocks for long-term success, making them indispensable for athletes at every level.







