In the world of elite sports, athletes are always seeking that extra edge to boost performance, improve recovery, and maintain optimal health. While traditional methods like rigorous training, balanced nutrition, and adequate rest are crucial, there’s a growing interest in exploring alternative techniques that can enhance physiological and psychological well-being. One such promising area is vagus nerve stimulation (VNS). This fascinating approach, rooted in both ancient practices and modern science, offers a unique pathway to unlocking athletic potential. In this comprehensive article, we’ll discuss the science behind VNS, its mechanisms, and its diverse benefits for athletes.
What is the Vagus Nerve?
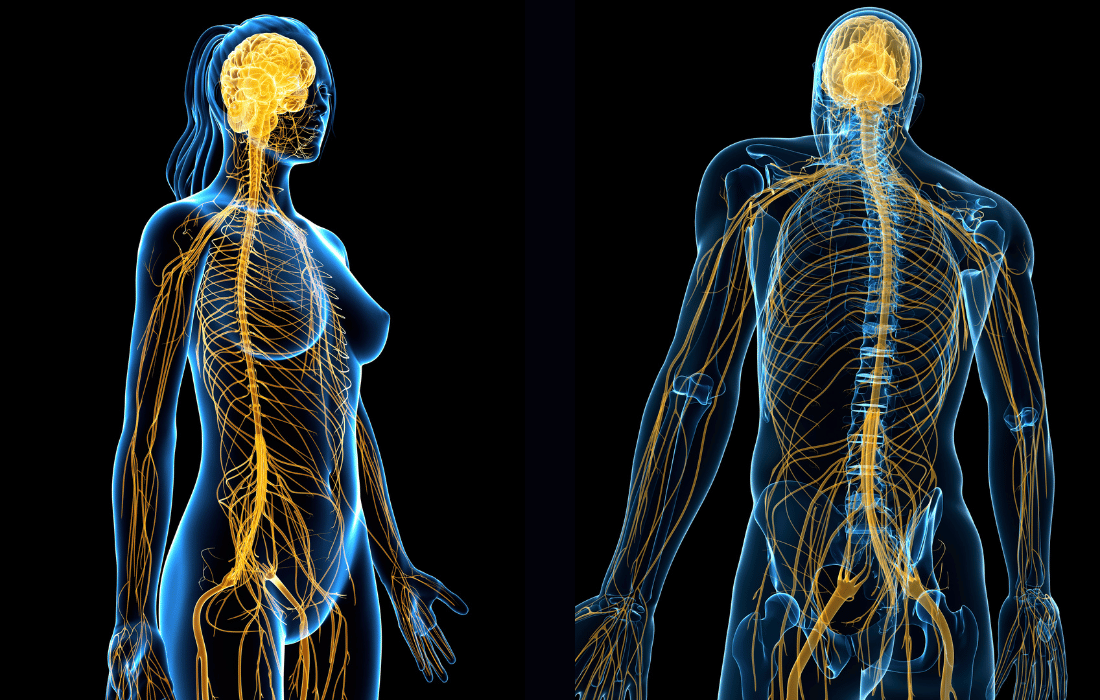
The vagus nerve, also known as the tenth cranial nerve, is one of the longest and most complex nerves in the human body. It extends from the brainstem down to the abdomen, innervating major organs such as the heart, lungs, and digestive tract. The term “vagus” is derived from the Latin word for “wandering,” aptly describing its extensive reach and influence throughout the body.
The vagus nerve plays a pivotal role in the parasympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the “rest and digest” functions that counterbalance the “fight or flight” responses of the sympathetic nervous system. This nerve regulates critical bodily functions, including heart rate, blood pressure, digestion, and immune response, making it a key player in maintaining homeostasis.
Mechanisms of the Vagus Nerve
Connection to the Central Nervous System
The vagus nerve serves as a major communication highway between the brain and the body. It originates in the medulla oblongata, a part of the brainstem, and extends down through the neck and thorax to the abdomen. This nerve is integral to the central nervous system (CNS), relaying information between the brain and various organs.
Neurotransmitter Release
VNS stimulates the release of neurotransmitters like acetylcholine and norepinephrine. Acetylcholine plays a crucial role in muscle activation and cognitive function, while norepinephrine enhances alertness and concentration. For athletes, this translates to improved focus, quicker reaction times, and better overall performance.
Heart Rate Variability (HRV)
HRV is a measure of the variation in time between each heartbeat, and it’s considered a marker of autonomic nervous system balance and vagal tone. Higher HRV indicates a healthy, resilient system capable of efficiently responding to stress. VNS has been shown to improve HRV, which can enhance an athlete’s ability to recover from intense training and reduce the risk of overtraining and injury.
Connection to the Gut
The vagus nerve is a critical component of the gut-brain axis, the bidirectional communication pathway between the gut and the brain. This connection influences mood, stress levels, and overall health. For athletes, a healthy gut-brain axis can improve digestion, nutrient absorption, and mental well-being, all of which are essential for peak performance.
Gut-Brain Axis and Nutrient Absorption
The vagus nerve plays a crucial role in regulating digestive processes. It influences the release of digestive enzymes and the motility of the gastrointestinal tract, which are vital for effective nutrient absorption. Proper nutrient absorption ensures that athletes get the necessary vitamins and minerals to fuel their bodies, repair tissues, and build muscle.
Mood Regulation
The gut produces about 90% of the body’s serotonin, a neurotransmitter that significantly influences mood. The vagus nerve helps modulate serotonin levels by regulating gut bacteria and ensuring a balanced gut microbiome. A healthy gut-brain connection can lead to better mood regulation, reducing anxiety and depression, which are common challenges athletes face.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects
One of the most significant benefits of VNS is its anti-inflammatory properties. By activating the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway, VNS helps regulate the immune system and reduce inflammation. Chronic inflammation can impair athletic performance and recovery, making this a valuable benefit for athletes.
Benefits of Vagus Nerve Stimulation for Athletes
Enhanced Recovery
Recovery is paramount for athletes, and VNS can play a significant role in speeding up this process. By promoting parasympathetic activity, VNS helps reduce muscle soreness, decrease inflammation, and enhance sleep quality. Improved recovery means athletes can train harder and more frequently without the risk of burnout or injury.
Stress Reduction
Athletes often face high levels of stress, both physically and mentally. VNS has been shown to reduce cortisol levels, the body’s primary stress hormone, and enhance overall relaxation. Lower stress levels can lead to better mental clarity, improved mood, and a greater ability to cope with the pressures of competition.
Improved Mental Focus and Cognitive Function
Mental acuity is just as important as physical prowess in sports. VNS can improve cognitive function by enhancing neurotransmitter activity and promoting neuroplasticity—the brain’s ability to adapt and change. This can lead to better decision-making, sharper focus, and improved strategic thinking during competition.
Boosted Immune Function
A strong immune system is crucial for athletes, who are often exposed to physically demanding environments that can increase susceptibility to illness. VNS has been shown to modulate immune function, reducing the risk of infections and helping athletes stay healthy throughout their training and competition schedules.
Better Cardiovascular Health
Cardiovascular health is essential for endurance and overall athletic performance. By improving HRV and promoting a healthy autonomic balance, VNS can enhance cardiovascular function, leading to better endurance, reduced fatigue, and improved overall performance.
Practical Applications of VNS for Athletes
Deep Breathing Exercises
Deep, diaphragmatic breathing is a simple yet effective way to stimulate the vagus nerve. Techniques such as box breathing (inhaling for four counts, holding for four counts, exhaling for four counts, and holding for four counts) can be incorporated into daily routines to promote relaxation and improve vagal tone.
Meditation and Mindfulness
Meditation and mindfulness practices have been shown to enhance vagal tone and reduce stress. Athletes can incorporate these practices into their training regimen to improve mental clarity, focus, and overall well-being.
Yoga
Yoga combines physical postures, deep breathing, and mindfulness, making it an excellent practice for stimulating the vagus nerve. Regular yoga practice can improve flexibility, reduce stress, and enhance recovery, all of which are beneficial for athletes.
Non-Invasive VNS Devices
For athletes looking for a more targeted approach, non-invasive VNS devices offer a practical solution. These devices can be used daily to stimulate the vagus nerve and promote its benefits without the need for surgical intervention.
Case Studies and Research
VNS in Endurance Athletes
A study published in the Journal of Sports Science & Medicine investigated the effects of VNS on endurance athletes. The researchers found that VNS improved HRV and reduced markers of inflammation, leading to enhanced recovery and performance in long-distance runners.
VNS and Cognitive Function
Another study, featured in Frontiers in Psychology, examined the impact of VNS on cognitive function in athletes. The findings indicated that VNS improved reaction times and decision-making skills, highlighting its potential to enhance mental performance in sports.
VNS and Stress Reduction
Research published in Psychoneuroendocrinology explored the effects of VNS on stress levels in athletes. The study showed that VNS significantly reduced cortisol levels and promoted a state of relaxation, which can be crucial for athletes dealing with the pressures of competition.
Personal Anecdotes
Athletes from various disciplines have started to incorporate VNS into their routines, sharing positive experiences and notable improvements in performance and recovery. For example, professional MMA fighter Sean O’Malley has spoken about using deep breathing techniques and mindfulness practices to enhance his mental game and overall well-being.
Conclusion
Vagus nerve stimulation represents a promising frontier in the quest for enhanced athletic performance and recovery. By leveraging the body’s natural mechanisms for relaxation, anti-inflammation, and cognitive enhancement, VNS offers a holistic approach to achieving peak performance. Whether through simple practices like deep breathing and yoga or advanced technologies like non-invasive VNS devices, athletes have a valuable tool at their disposal to optimize their training, reduce stress, and improve overall health.
As research continues to unveil the full potential of VNS, its integration into athletic training regimens is likely to grow. By understanding and harnessing the power of the vagus nerve, athletes can unlock new levels of performance and resilience, ensuring they stay at the top of their game.
For those interested in exploring VNS further, numerous resources and devices are available to help you get started. Embrace this innovative approach and experience the transformative benefits of vagus nerve stimulation for yourself.
Given the potential and interest in this area, a comprehensive review article on vagus nerve stimulators might be a necessary endeavor soon to evaluate and compare the various devices and methods available.
Have a question or want to leave us a word? Leave us a comment down below!